Are points which seperateand isolate expansion sections constituted on the pipe system. In simple words, they are junction points which carry the emerging loads on the pipe section. It can be made in various forms but location is very important related to the operation of the expansion joint. ; Long piping systems are divided into shorter expanding sections, and isolated by main anchors. Thus the movements in the individual expanding sections are absorbed by the axial expansion joints in this section.
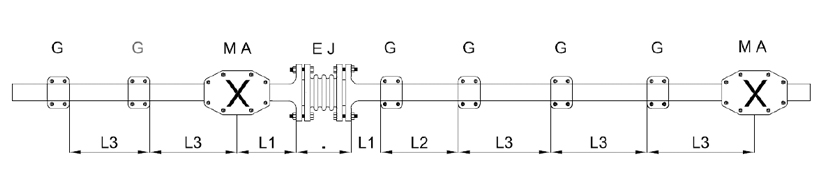
MA ( Fixed Point-Main anchor )
G ( Sliding Support-Guide )
L1 =4 .D
L2 =14 .D D = Diameter
L3 =See Thermal Expansion Table
FMA=Fi+Fy+Fs+Fd (kg)
FMA=Load of fi xed point
Fi=Load arrising from internal pressure
Fi=Pw . A Pw=Working Pressure (kg/mm2)
A=Pipe ınternal Cross Section Area (mm2)
Fy=Force arrising from bellow swing
Fy=Cy Δx/2
C=Bellow Axial Springrate (kg/mm)
X=Max Movement Amount (mm)
Fs= Sliding Support Friction Load
Fs=M.G.L
M=Friction Coeffi cient
G=Pipe Total Weight (kg/m)
L=Pipe Lenght(m)
Fd=Centrifugal If the fi xed in on the elbow
Fd= (2A.φ.V2)/g sin θ/2
A=Pipe Internal Cross section Area (m²)
φ=Density of Fluid (kg/m³)
V=Flow Velocity (m/sec)
g=Gravity Acceleration (m/sec²)
θ=Elbow Angle